 Home
Home
 Back
Back
A flow rate calculator is a tool used to determine the volume or mass of a fluid that passes through a specific point in a system per unit of time. To use this calculator, you need to input details such as the cross-sectional area of the pipe or channel, the velocity of the fluid, and the fluid's density (if calculating mass flow rate). Additionally, some calculators may ask for information on the type of fluid, the pressure, and the temperature to account for variations in fluid behavior. Based on these inputs, the flow rate calculator will compute the volumetric flow rate (e.g., liters per second or cubic meters per hour) or the mass flow rate (e.g., kilograms per second). This tool is essential for designing and optimizing systems in fields such as plumbing, HVAC, chemical engineering, and environmental science, ensuring efficient and accurate fluid management.
Flow rate refers to the volume of fluid that passes through a specific point in a system per unit of time. It is typically measured in units like liters per second (L/s), gallons per minute (GPM), or cubic meters per hour (m³/h). Flow rate is a key parameter in fluid dynamics, as it helps determine the efficiency and performance of systems involving liquids or gases.
The formula for calculating flow rate is:
Flow Rate (Q) = Volume (V) / Time (T)
Where:
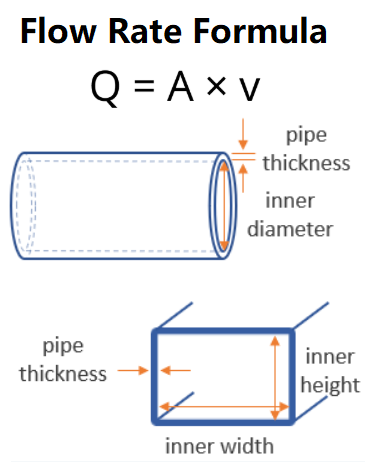
Problem: A round pipe (diameter 25 mm) carries water at 10 m/s. Calculate the flow rate.
A = π × (25 mm / 2)² = 3.1416 × 12.5² ≈ 490.875 mm²
Convert to m²: 490.875 mm² ÷ 1,000,000 = 0.000490875 m²Q = A × v = 0.000490875 m² × 10 m/s = 0.00490875 m³/s
Convert to m³/h: 0.00490875 × 3600 = 17.6715 m³/hMass Flow = 17.6715 m³/h × 1000 kg/m³ = 17,671.5 kg/h (17.6715 t/h)
Problem: A rectangular pipe (2 cm × 4 cm) carries gas at 15 m/s. Calculate the discharge rate.
A = width × height = 2 cm × 4 cm = 8 cm²
Convert to m²: 8 cm² ÷ 10,000 = 0.0008 m²Q = A × v = 0.0008 m² × 15 m/s = 0.012 m³/s
Convert to L/s: 0.012 × 1000 = 12 L/s12 L/s × 3600 = 43,200 L/h
Flow rate plays a vital role in many applications, including:
Several factors can influence flow rate, including:
Since most systems work in gallons per minute (GPM), you may need to convert cubic feet per second to GPM. To do this, multiply the cubic feet per second by 7.481 (to convert to gallons) and then by 60 (to convert to minutes):
Q (GPM) = Q (ft³/sec) × 7.481 × 60
Water pressure and other factors can influence the total flow volume, but generally, pipes have average flow rates. The following chart assumes both minimum and maximum pressures within the pipe:
| Pipe Diameter | Average GPM |
|---|---|
| 1″ | 16 – 58 |
| 1 1/2″ | 35 – 126 |
| 2″ | 55 – 200 |
| 3″ | 140 – 425 |
| 4″ | 240 – 700 |